November 1, 2023, Pushpinder Puri, 7 Mins
Life expectancy significantly indicates a nation’s overall health and well-being. It reflects the average number of years a person can expect to live based on current mortality rates. In Canada, a country known for its high quality of life, universal healthcare system, and diverse population, life expectancy has steadily increased over the years. This comprehensive guide will delve into the factors influencing life expectancy in Canada, its historical trends, and the various demographic and health-related aspects that contribute to the nation’s impressive average life expectancy.
Let’s Understand Life Expectancy
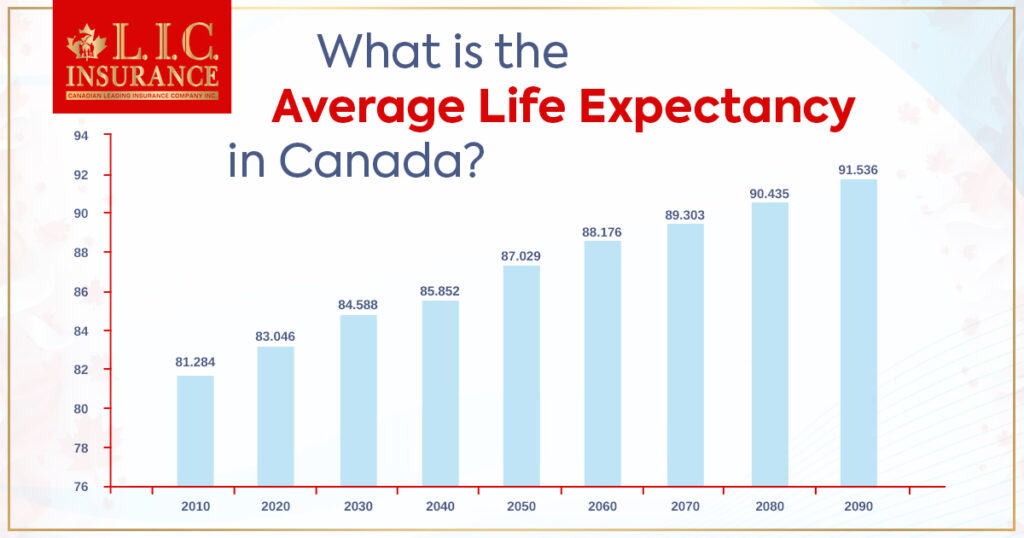
The Historical Trend of Life Expectancy in Canada
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy in Canada
Regional Variations in Life Expectancy
What’s the most common cause of death in Canada?
Why is Canada’s life expectancy so high?
Is wealth related to life expectancy in Canada?
What does life expectancy in Canada have to do with life insurance?
Life expectancy is a statistical measure used to estimate the average number of years a person born in a specific year can expect to live, assuming that current mortality rates remain constant throughout their lifetime. It is typically calculated based on data related to mortality, age-specific death rates, and various demographic factors.
Life expectancy in Canada has shown a consistent upward trend over the past century, thanks to improvements in healthcare, sanitation, nutrition, and living conditions. Key milestones in Canada’s life expectancy history include:
Several key factors contribute to the high average life expectancy in Canada:
While Canada boasts a high average life expectancy, there are regional variations within the country. Life expectancy can vary by province, territory, and even by specific cities or communities.
Some of the key factors influencing these regional variations include:
Efforts are ongoing to address these regional disparities and ensure that all Canadians have the opportunity to live long and healthy lives, regardless of where they reside.
While Canada’s life expectancy continues to rise, it is not without challenges:
As of September 2021, the most common causes of death in Canada were generally related to chronic diseases and conditions. However, it’s important to note that the prevalence of specific causes of death can change over time due to various factors, including advances in healthcare and changes in lifestyle.
Common causes of death in Canada at that time included:
For this reason, Canadian LIC highly advises that Canadians purchase Critical Illness Insurance. The likelihood of developing cancer makes it unnecessary to go without a plan to safeguard your family in the event of the unexpected.
It’s essential to consult the latest data and reports from organizations such as Statistics Canada or the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) to obtain the most current information on the leading causes of death in Canada, as trends can evolve over time due to public health efforts and advancements in medical care.
Canada’s high life expectancy can be attributed to a combination of factors, including its healthcare system, socio-economic conditions, lifestyle, and public health efforts. Here are some key reasons why Canada has a relatively high life expectancy:
Canada’s overall life expectancy is relatively high, and there can be regional variations within the country due to differences in socio-economic conditions, healthcare access, and lifestyle choices. There are continuous initiatives to deal with these regional disparities and guarantee that all Canadians have the chance to lead long and healthy lives.
In Canada, wealth is indeed related to life expectancy, but the relationship is complex and influenced by various factors. Here are some key considerations:
However, it’s crucial to recognize that the relationship between wealth and life expectancy is not absolute. Canada’s universal healthcare system aims to provide equitable access to healthcare services for all residents, regardless of income. Additionally, social policies and public health efforts in Canada aim to reduce health disparities and promote well-being among all citizens.
Efforts to address health inequities and improve access to healthcare and education are ongoing in Canada to ensure that individuals from all socio-economic backgrounds have the opportunity to live longer, healthier lives.
Life expectancy in Canada is a relevant factor in the context of life insurance because it helps insurance companies assess risk and determine premiums for policyholders. Here’s how life expectancy is related to life insurance:
So, life expectancy is a crucial factor in the insurance industry because it helps insurers assess the financial risks associated with providing coverage. The longer a person is expected to live, the less risk there is for the insurer, potentially resulting in lower premiums for policyholders.
Conversely, individuals with factors that may reduce their life expectancy may face higher premiums or different policy terms.
Hence, Canada’s average life expectancy reflects a nation committed to the well-being of its citizens and residents. The country’s investment in healthcare, education, social programs, and environmental stewardship has contributed to a steadily increasing life expectancy. However, challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to healthcare and addressing the needs of an aging population. As Canada continues to evolve, its commitment to health and well-being will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of life expectancy in the nation.
To learn more about life insurance, visit our blog page. If you’re considering how you may best financially secure your family in the future, you can also schedule a call with one of our experienced insurance brokers.
Now we come to some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the average life expectancy in Canada:
As of the early 2020s, the average life expectancy in Canada is approximately 82 years.
Canada’s life expectancy is among the highest in the world and is on par with other developed countries with advanced healthcare systems.
Canada’s high life expectancy is influenced by factors such as universal healthcare, healthier lifestyles, access to advanced medical technology, and a strong economy.
Yes, there are regional variations in life expectancy within Canada. Life expectancy can vary by province, territory, and even by specific cities or communities. Socioeconomic factors, access to healthcare, and lifestyle choices can contribute to these variations.
Canada’s life expectancy has steadily increased over the past century. In the early 1900s, it was around 50 years, but it has since risen due to improvements in healthcare, sanitation, nutrition, and living conditions.
Canada’s publicly funded healthcare system ensures that citizens and residents have access to necessary medical services without high healthcare costs. Regular medical check-ups, early disease detection, and timely treatment contribute to longer life expectancies.
Challenges include addressing the needs of an aging population, addressing mental health issues, ensuring equitable access to healthcare services, and managing the rise of chronic diseases.
Efforts are ongoing to address regional disparities through initiatives to improve socioeconomic conditions, increase healthcare access in underserved areas, and promote healthier lifestyles.
Canada’s multicultural society promotes social cohesion and inclusivity, which can positively impact mental and emotional health and contribute to longer life expectancies.
While it’s difficult to predict with certainty, Canada’s commitment to healthcare, education, and well-being suggests a continued focus on maintaining and potentially increasing life expectancy in the future.
The number of Canadians living to be 100 years old, often referred to as centenarians, was steadily increasing due to advancements in healthcare and overall improvements in living conditions as of September 2021. However, the specific number of centenarians can vary from year to year, and the most accurate and up-to-date data can be obtained from Statistics Canada, the country’s national statistical agency.
Statistics Canada typically releases demographic information, including the number of centenarians, in its census reports and demographic studies. To obtain the latest and most precise figures regarding the population of centenarians in Canada, I recommend visiting the official website of Statistics Canada or referring to their publications and reports on demographics and aging.
The above information is only meant to be informative. It comes from Canadian LIC's own opinions, which can change at any time. This material is not meant to be financial or legal advice, and it should not be interpreted as such. If someone decides to act on the information on this page, Canadian LIC is not responsible for what happens. Every attempt is made to provide accurate and up-to-date information on Canadian LIC. Some of the terms, conditions, limitations, exclusions, termination, and other parts of the policies mentioned above may not be included, which may be important to the policy choice. For full details, please refer to the actual policy documents. If there is any disagreement, the language in the actual policy documents will be used. All rights reserved.
Please let us know if there is anything that should be updated, removed, or corrected from this article. Send an email to [email protected] or [email protected]